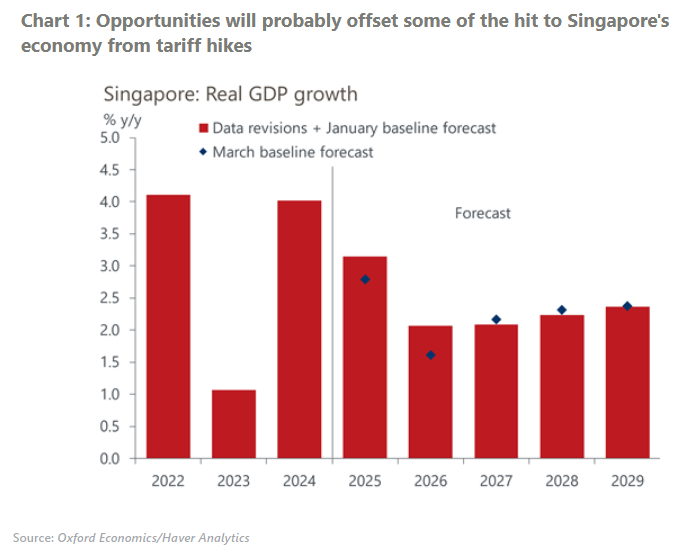
Opportunities in Singapore could mitigate hit from US trade barriers
The slew of tariff proposals coming out of the US has added much uncertainty to the highly export-reliant Singapore economy. Given its status as a major shipping hub, potential gains from trade rerouting will probably offset some of the negative impacts of increased tariffs. The upshot is that although Singapore’s prospects are dimmed, they remain relatively promising.
What you will learn:
- Singapore runs a trade deficit with the US and imposes lower tariffs on US imports due to the US-Singapore Free-Trade Agreement, meaning the threat of reciprocal tariffs is low. However, if Trump disregards the FTA, US tariffs on Singapore imports could rise to 0.71%, with specific goods like semiconductors and pharmaceuticals facing an additional 0.75%, bringing the total to 1.5%.
- Indirect effects could pose a greater risk to Singapore, as potential tariffs may impact trade and business decisions. Second-round effects from higher tariffs on trade partners could reduce demand for goods, affecting trade flows through Singapore.
- On the upside, the US’ competitive disadvantage in chip production may lower semiconductor tariff risks, while Singapore could benefit from trade rerouting away from China. Singapore is likely to gain US import share over the next decade as other countries lose theirs.
Tags:
Related Posts

Airbnb’s Economic Contribution to APAC in 2024: GDP, Jobs, and Regional Impact
Airbnb's platform connects hosts across Asia Pacific (APAC) with travellers from around the world. Oxford Economics was commissioned by Airbnb to quantify its economic footprint in 10 APAC markets in 2024.
Find Out More
New Rules of Engagement: The Strategic Rise of Government Affairs in Asia
What’s behind Asia’s new era of policy assertiveness? What does it mean for international firms?
Find Out More
25% auto tariffs especially painful in Japan and South Korea
US tariffs of 25% on all automobile and auto parts will weigh heavily on the Japanese and South Korean automotive sectors. A GTAP analysis suggests Japanese and South Korean automotive production will each shrink by approximately 7%. The impact is larger than suggested by bilateral trade data, because vehicles assembled in other countries before being shipped to the US will also be affected, dampening domestic auto parts production.
Find Out More