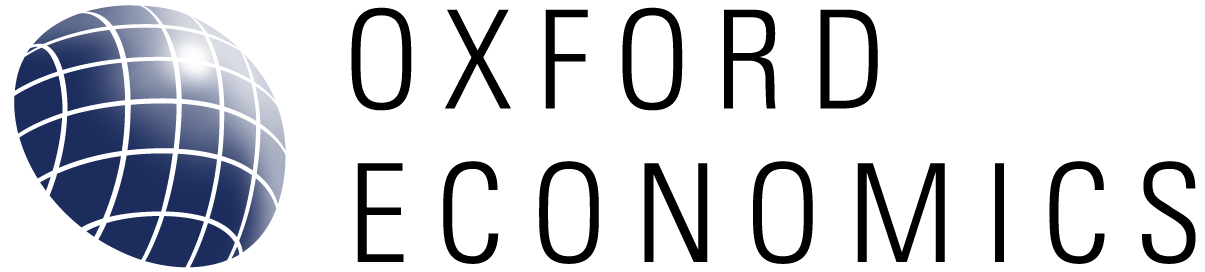Japan fiscal rigidity intensifies with fast-aging and soaring debt
The effective size of the FY2024 initial budget continues to expand, led by structural pressures from fast-aging, rising debt servicing costs, and the increasing needs for defence spending. Fiscal rigidity has intensified as the government has no intention to hurry fiscal consolidation.
What you will learn:
- Social security expenses, which account for one-third of the budget, rose by 1 trillion yen from FY2023. Higher interest rates increased debt servicing costs by 2 trillion yen, reaching almost one-fourth of the budget. National defence spending rose by 1 trillion yen, following the government’s plan to double its size in five years to 2% of the GDP by 2027.
- Tax revenues are expected to remain the same as in FY2023, as political decision to cut income tax temporarily to support households will offset the additional revenue induced by an economic recovery.
- Although the FY2024 budget foresees a visible improvement in the primary balance, we are doubtful of its feasibility, given that it has become customary to have a sizeable supplementary budget at year-end in recent years regardless of economic conditions.
- The effective primary fiscal deficit during the pandemic was much smaller than budget figures and returned to balance in a short period because of the unspent amount and a rising share that is transferred to strategic funds which are not spent immediately
Tags:
Related Posts
Post
Tariffs and Politics Leave the BoJ Powerless in Japan
The Bank of Japan kept its policy rate at 0.5% at its July meeting. We continue to think the BoJ will exercise caution on rate hikes despite still-high inflation and a recent trade deal with the US.
Find Out More
Post
US-Japan Trade Deal Fails to Shift Japan’s Growth Outlook
We estimate that the US's effective tariff rate on Japanese products is around 17%, in line with our baseline assumption. Lower tariffs on autos are a positive, given the sector's significant contribution to the economy and its broad domestic supporting base
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s Rising Political Instability Will Undermine Fiscal Discipline
The ruling Liberal Democratic party (LDP) and its partner Komeito lost their majority in Japan's upper house elections on July 20. Although Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba will likely stay to avoid political gridlock, especially to complete tariff negotiations with the US, the political situation has become fluid and could lead to a leadership change or the reshuffling of the coalition.
Find Out More