Japan: The impact of structural labour shortages on inflation

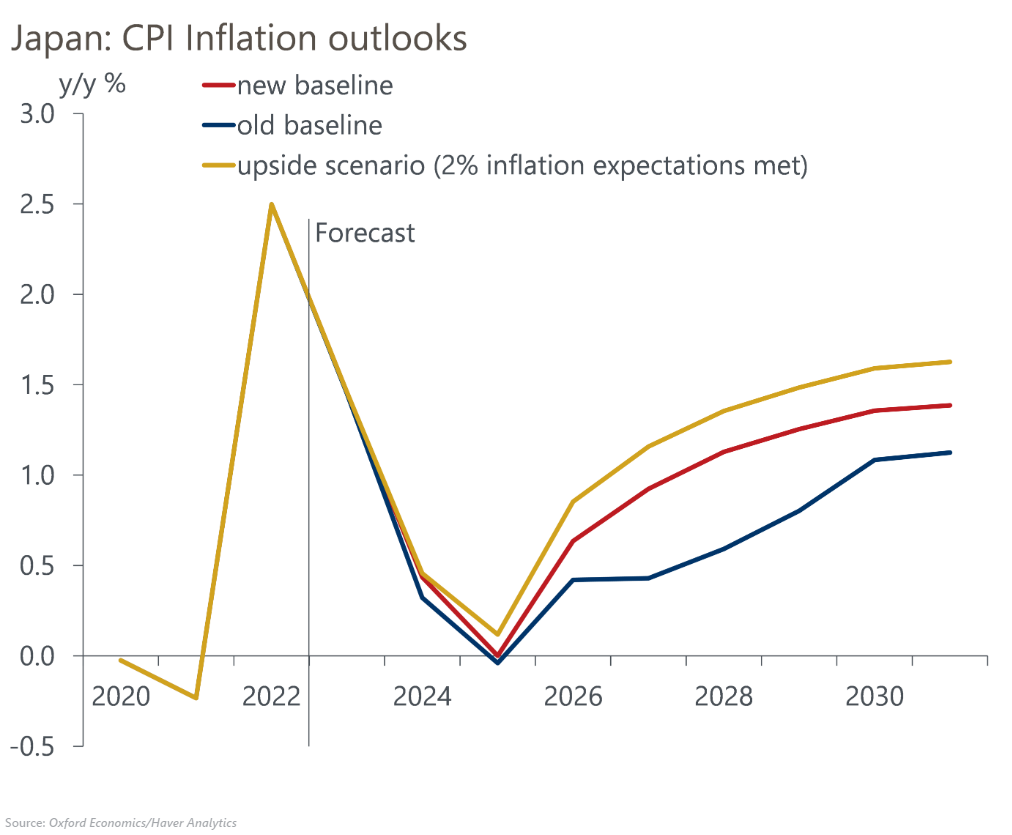
We have revised up our long-term wage and inflation projections based on a larger impact from structural labour shortages due to adverse demographic trends. Even after raising our wage growth assumptions by 0.5ppts on average over 2024-2030, however, we still forecast inflation only reaching 1.4% in 2030 – well short of the 2% target.
What you will learn:
- We now project higher base-wage increases for regular workers. We assume that wage growth set in the annual spring negotiations will rise gradually to 3% by 2030 from an average of 2.3% in the five years before the pandemic. Despite the rising need for wage increases to secure talented workers, Japan’s rigid employment system will constrain pay growth.
- We also revised up our projection for the hourly wage for part-time workers, which is more elastic to labour market conditions than wages for regular workers. We project hourly wages to increase as fast as in the late 2010s this year and then to accelerate, reaching close to 4% by 2030 due to the limited pool of additional labour supply.
- Gradual but persistent wage rises will boost inflation expectations accordingly. Given that Japan’s inflation expectations tend to be formed adaptively, we believe that inflation expectations will rise in accordance with actual price developments. In our baseline, we assume that inflation expectations will rise only gradually to 1.5% in 2030 from 1.1% in 2022.
Tags:
Related posts
Post
Tariffs and Politics Leave the BoJ Powerless in Japan
The Bank of Japan kept its policy rate at 0.5% at its July meeting. We continue to think the BoJ will exercise caution on rate hikes despite still-high inflation and a recent trade deal with the US.
Find Out More
Post
US-Japan Trade Deal Fails to Shift Japan’s Growth Outlook
We estimate that the US's effective tariff rate on Japanese products is around 17%, in line with our baseline assumption. Lower tariffs on autos are a positive, given the sector's significant contribution to the economy and its broad domestic supporting base
Find Out More
Post
Japan’s Rising Political Instability Will Undermine Fiscal Discipline
The ruling Liberal Democratic party (LDP) and its partner Komeito lost their majority in Japan's upper house elections on July 20. Although Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba will likely stay to avoid political gridlock, especially to complete tariff negotiations with the US, the political situation has become fluid and could lead to a leadership change or the reshuffling of the coalition.
Find Out More